Why Textbooks May Need to Update What They Say About Birth Canals
A new study shows that the structure of the human pelvis varies between populations, which could have implications for how babies are birthed.

By Steph Yin
Look up the term “pelvic canal” in the typical anatomy or obstetric textbook, and you likely will find a description such as this: “Well-built healthy women, who had a good diet during their childhood growth period, usually have a broad pelvis.”
Such a pelvis, the text continues, enables “the least difficulty during childbirth.”
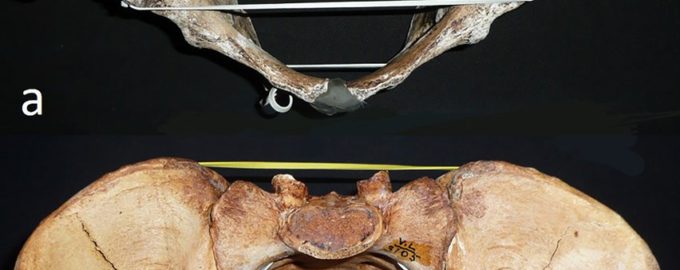
But such characterizations have long been based on anatomical studies of people of European descent. In reality, the structure of the pelvic canal, the bony structure through which most of us enter the world, varies tremendously between populations, according to a new study in Proceedings of the Royal Society B.
The findings have implications for how obstetricians treat patients of color, the authors say. In the United States, racial disparities in maternal health care are prevalent. Compounding factors like interpersonal and institutional racism, poverty, poor health care access and environmental burdens disproportionately harm black mothers. These contribute to the risk of pregnancy-related deaths being three to four times higher for black women than for white women.
Limited prescriptions of what constitutes a “normal” pelvis or birthing process might lead doctors to perform unnecessary interventions — like induced labor, cesarean sections or the use of forceps — which can further exacerbate harm, said Lia Betti, an anthropologist at the University of Roehampton in London, and the study’s lead author.
“What worries me is that doctors come out of school thinking of the European model of the pelvis,” Dr. Betti said. In the early 1900s, this led to “horrific situations” in which American doctors used forceps on black mothers, trying to force babies to align with “the rotation pattern for a European classical pelvis,” she added.
Modern humans have narrow pelvises compared to the size of babies’ heads. That discrepancy contributes to higher rates of birthing complications in humans than in other primates.
There is no accepted explanation for why the human pelvis leaves such little room for childbirth. Dr. Betti and her colleague Andrea Manica, of the University of Cambridge, set out to study a classic if highly-contested explanation known as the “obstetrical dilemma” hypothesis.
The dilemma posits that as our species evolved and began walking upright, the width of the human pelvis narrowed, enabling the body’s weight to stay closer to its center of gravity. But as humans also developed bigger brains, it became harder for a fetus’s skull to squeeze through that tight channel.
To explore the idea, she and Dr. Manica measured 348 skeletons from around the world. They found that pelvic shape varied enormously, even more than measures of leg, arm and general body proportion that are known to vary significantly between populations. That was “remarkable and unexpected,” the researchers wrote.
Mostly, they found, pelvic shape varied along lines of geographic ancestry. People of sub-Saharan origin generally had the deepest pelvises back-to-front, while Native Americans had the widest side-to-side. Europeans, North Africans and Asians fell in the middle of the range.
Birth-canal shape also varied markedly within populations, although the variation decreased the farther a population originated from Africa. That finding is consistent with others indicating that a population’s genetic diversity declines the farther it moves from the cradle of humankind
Most of that variation in pelvic shape stemmed from random fluctuations in gene frequency, although natural selection seems to have played a minor role as well, Dr. Betti said. The top of the birth canal is slightly wider in populations from colder climates, perhaps to help make the body stockier.
The variation observed by Dr. Betti suggests that pelvic shape is not so strictly controlled. And if pelvic shape is highly variable across populations, it’s likely “that the birthing process is also highly variable,” said Helen Kurki, an anthropology professor at the University of Victoria in Canada.
These findings challenge the idea “that there is one ‘right’ way to birth a baby,” Dr. Kurki said, and suggest that a more individualized approach to childbirth might be better.
Although people differ from one another anatomically, Dr. Betti said, her research suggests that those differences are not always functional.
“If you look at the shape of the birth canal in different people, it could be tempting to think it’s adapted to give birth to babies with differently-shaped heads, or something like that,” she said.
“In fact, the differences are mostly by chance, which I think is beautiful. Sometimes human variation is just random.”